Web2’s grip on mobile apps is loosening. Fast. And Web3 is changing how iOS apps get planned, coded, and used, instead of parking everything on one company’s servers, you’re dealing with decentralized networks, on-chain visibility, token-based incentives, and the idea that people actually own their stuff.
For businesses, that shift creates a bunch of new directions. DeFi apps. NFT markets. Wallets. Decentralized products. And identity tools that don’t rely on one gatekeeper. But here’s the catch: you can’t build these like a normal “backend and app store” project, and you can’t fake your way through the architecture either, because Web3 comes with different assumptions and different points (fees, key management, chain quirks, all of it)—which is why working with an experienced iOS application development company matters more than ever.
So what’s this guide trying to do? It lays out what you need for Web3 iOS app development, core ideas, the toolchains people use, where the industry seems to be heading, and why decentralized identity (DID) keeps coming up in real product conversations. Short version: Know the map before you start wandering.
Web3 Explained: Key Concepts and Its Evolution Over Time
Web3’s basically the next phase of the internet, where you, not some company in the background, get more say over your online identity, your data, and the digital stuff you own. And instead of one central group running everything, these apps run on distributed networks, which means the rules live in the system itself, transactions can happen automatically, and people can interact without needing to “trust” a middleman (yeah, it sounds a little weird first).
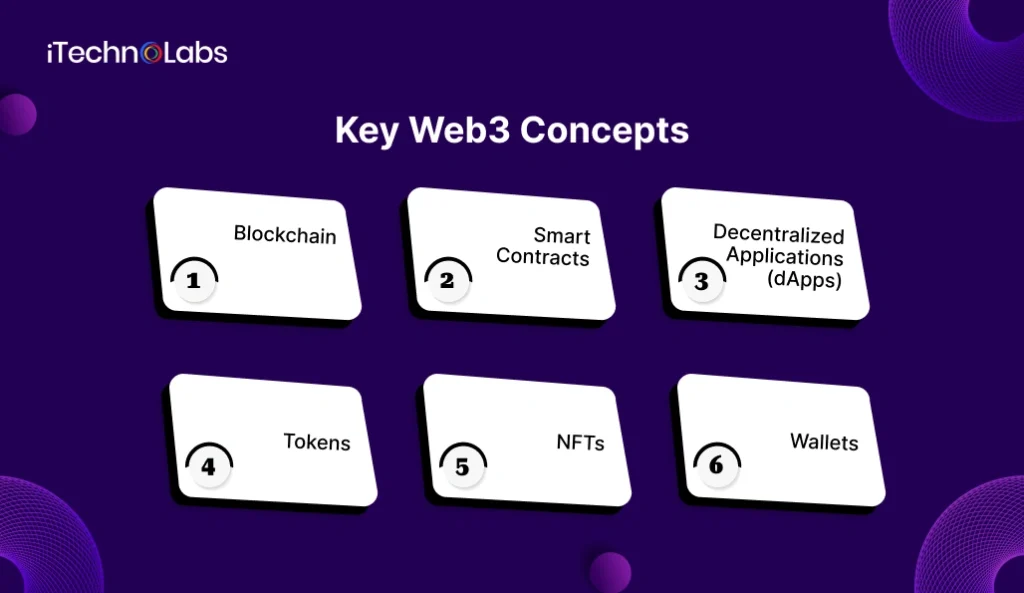
Key Web3 Concepts
To understand Web3, it is essential to learn the core technologies that make decentralized applications possible. Web3 is not just about cryptocurrency, it is a complete ecosystem built on decentralized networks where users can own assets, control identity, and interact securely without relying on centralized intermediaries.
Below are the most important building blocks of Web3 explained in detail.
Blockchain
Blockchain is a decentralized digital ledger that records transactions securely across a network of computers. Instead of relying on one central authority, blockchain distributes data to multiple nodes, ensuring transparency and trust. Once data is added, it becomes extremely difficult to change, making blockchain ideal for secure Web3 applications.
- Works on a distributed network (nodes)
- Stores data in blocks linked as a chain
- Provides high transparency and traceability
- Prevents tampering due to immutability
- Enables trust without third-party control
Smart Contracts
Smart contracts are self-executing programs stored on a blockchain. They automatically perform actions when specific conditions are met, such as sending tokens or issuing NFTs. Smart contracts remove the need for intermediaries, reduce manual processing, and increase reliability because transactions follow coded rules that cannot be easily altered.
- Runs automatically on blockchain
- Executes based on set conditions
- Eliminates middlemen in transactions
- Used for DeFi, NFTs, staking, governance
- Requires strong security testing before launch
Decentralized Applications (dApps)
Decentralized applications (dApps) are apps that operate on blockchain infrastructure rather than centralized servers. They use smart contracts for backend logic, enabling transparent and user-controlled experiences. dApps often allow wallet-based login, token transactions, and digital asset ownership, making them a key component of modern Web3 ecosystems.
- Built on blockchain-based infrastructure
- Uses smart contracts for app functionality
- Often supports wallet login instead of passwords
- Enables transparent, verifiable transactions
- Common in DeFi, gaming, and NFT marketplaces
Tokens
Tokens are cryptographic digital assets that exist within blockchain networks. Their applications include payment, rewards, voting, and rights to access the platform. Tokens are the driving force behind Web3 economies, facilitating the transfer of value not only between users but also through various applications. Additionally, they grant communities the power to decide and keep the activity going through rewards in the decentralized ecosystem.
- Used for transactions and payments
- Supports rewards and loyalty models
- Can provide governance/voting rights
- Drives user participation and incentives
- Works across multiple blockchain networks
NFTs
NFTs (non-fungible tokens) are unique digital assets stored on the blockchain that prove ownership and authenticity. Unlike cryptocurrencies, NFTs are not interchangeable because each one is distinct. NFTs are widely used in digital art, gaming, memberships, and ticketing, giving users real ownership in digital environments.
- Unique and non-interchangeable asset
- Proves ownership and authenticity
- Used in art, gaming, tickets, memberships
- Enables trading and resale on marketplaces
- Supports token-gated access and rewards
Wallets
Wallets are Web3 tools that store cryptographic keys used to access blockchain assets and approve transactions. A wallet acts like a user’s Web3 identity, enabling them to connect with dApps, hold tokens, and sign secure transactions. Wallets can be external or embedded inside mobile applications.
- Stores private/public keys securely
- Used for signing transactions on blockchain
- Works as login/identity for Web3 apps
- Connects users to dApps and marketplaces
- Can be external (MetaMask) or embedded wallets
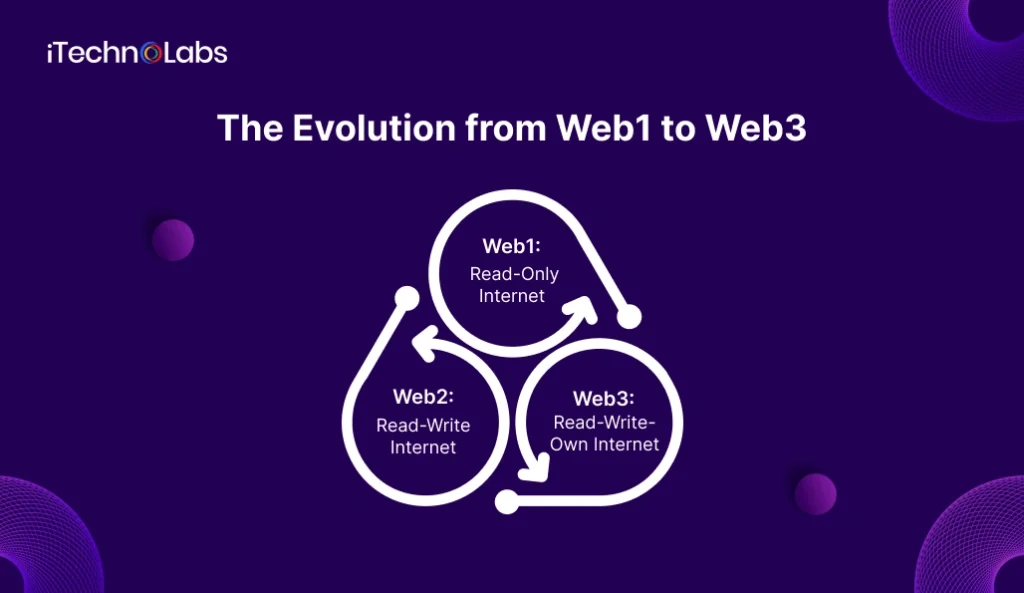
The Evolution from Web1 to Web3
Web3 is not a sudden innovation, it is the result of how the internet has evolved over time. The journey from Web1 to Web2 and now Web3 shows a clear shift from simple information access to interactive platforms and finally to user ownership. This evolution is also accelerating Web3 iOS App Development, helping businesses build decentralized, future-ready products.
Web1: Read-Only Internet
Web1 was the first stage of the internet where users mainly consumed information. Websites were static, with limited interaction and no personalization. Businesses used Web1 mostly to publish content and basic pages. Users could read what was available, but they could not contribute, engage, or create digital communities.
- Static websites with basic content
- Minimal interaction and user engagement
- No social media or user-generated content
- Mostly informational pages (read only)
- Limited personalization and functionality
Web2: Read-Write Internet
Web2 introduced interactive platforms that allowed users to create and share content. Social media, eCommerce, SaaS tools, and mobile apps grew rapidly. However, Web2 platforms are centralized, meaning companies own user data and control the system. This created concerns about privacy, transparency, and control over digital identity.
- Users can create and share content
- Rise of social media and SaaS platforms
- Centralized control by big companies
- User data stored in private servers
- Privacy and data ownership concerns
Web3: Read-Write-Own Internet
Web3 is the next evolution of the internet, where users own their digital identity, assets, and data. It uses blockchain, smart contracts, and decentralized networks to enable peer-to-peer interactions without intermediaries. Users can participate through tokens, NFTs, and decentralized identity, making digital ecosystems more transparent and community-driven.
- Ownership of assets via tokens and NFTs
- Wallet-based identity instead of passwords
- Decentralized control without intermediaries
- Smart contracts automate transactions securely
- Greater transparency and user control
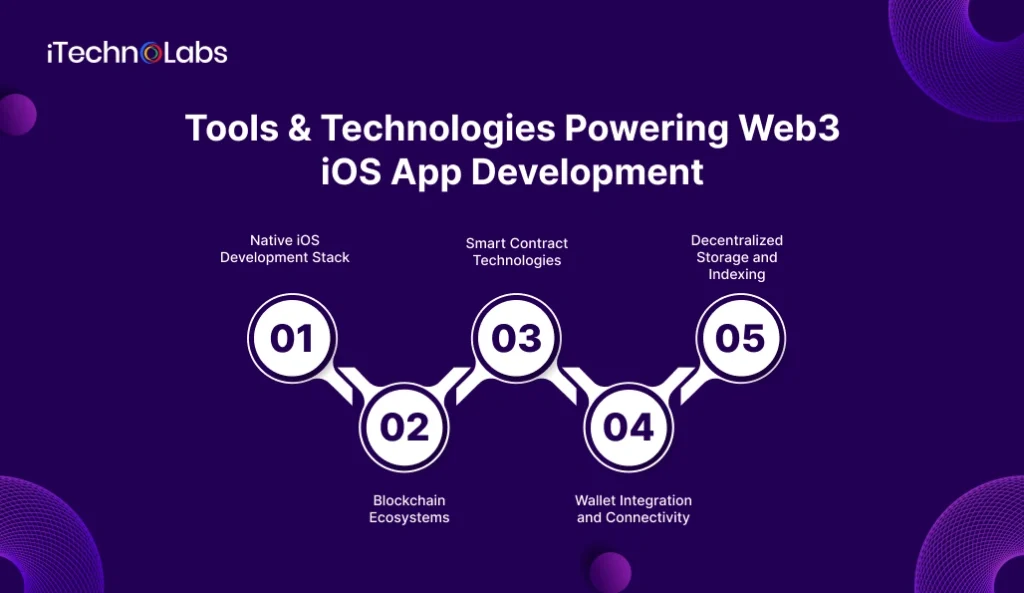
Tools & Technologies Powering Web3 iOS App Development
To build a high-performing and secure Web3 iOS application, developers need a mix of native iOS technologies and blockchain infrastructure. Unlike regular mobile apps that rely only on APIs and databases, Web3 apps must interact with blockchains, wallets, smart contracts, and decentralized storage networks.
Below is a clear breakdown of the key technologies that shape modern Web3 iOS App Development.
Native iOS Development Stack
Web3 apps end up touching some pretty sensitive stuff, signing transactions, juggling private keys, and checking who a user really is. That’s not the way to cut corners. And that’s why going native on iOS matters: the app runs faster, the interface feels less “laggy,” and you’ve got a tighter grip on security.
So what tools do people actually use? A lot, but a few show up constantly, especially when your wallet flows and anything that asks the user to approve a transaction (because that screen can’t be sketchy).
- Swift and SwiftUI usually sit at the center of it. Swift is Apple’s main language, and SwiftUI helps you build clean, modern screens without fighting layout code all day. Short: it’s great for wallet home pages, token lists, transaction prompts, and those dashboard-style views people stare at for hours.
- But UIKit isn’t dead. Not even close. And if you’ve ever tried to do custom interactions in SwiftUI, you know why: UIKit still gives you more precise control when you need tricky animations, complicated navigation, or a UI that has to feel “just right” under your thumb. Plenty of serious Web3 apps still lean on UIKit for the harder screens.
- Then there’s CryptoKit. This is the built-in crypto framework for things like hashing, encryption, and signing data. In a Web3 context, it can, with secure authentication steps, make the parts around transactions and identity less (because nobody wants to find out the security was duct-taped together after the fact).
So, what’s the point? Native iOS tech, Swift/SwiftUI, UIKit, and CryptoKit let the app stay smooth while it handles the scary, security-heavy blockchain actions users actually care about.
Blockchain Ecosystems
Picking a blockchain isn’t some tiny setup choice. It hits everything. And yeah, it changes what users feel day to day, fees, how fast stuff goes through, how well the app holds up when traffic spikes, all of it.
Here are the usual suspects people keep coming back to, for better or worse. So what are you actually building?
- Ethereum: It’s the old standby, and it still runs a huge chunk of Web3, especially DeFi and anything heavy on smart contracts. The dev community is massive, and the tools are mature, but the tradeoff is pretty obvious: gas can get painfully expensive when the network gets busy. And sometimes it’s busy a lot.
- Polygon: This one exists because Ethereum can get clogged. Polygon stays with Ethereum, but it tends to push transactions through quicker and for way less money, which is why teams use it when they want to keep one foot in Ethereum’s world without charging users an arm and a leg (or scaring them off on the first click).
- Solana: Speed is the headline here. It’s cheap too. But it doesn’t feel like Ethereum under the hood, and that matters, different tooling, different dev habits, different expectations, so if your team lives in Solidity land, there’s a learning curve. Still, it shows up a lot in NFT markets and apps where waiting around even a few seconds feels like friction.
- Avalanche and BNB: These two get picked when projects want quick confirmations and room to without things getting sluggish. They show up all over DeFi, gaming, and token-heavy platforms, and teams usually like them because they can move fast without the fee drama you sometimes see elsewhere. Not perfect. Just practical.
So what’s the priority, maximum adoption and network effect (Ethereum), everyday use while staying close to Ethereum (Polygon), raw speed and low cost (Solana), or a chain that’s built for high-throughput DeFi-style apps (Avalanche/BNB)? Pick based on that, hype.
Smart Contract Technologies
Smart contracts sit at the “rules” layer in a Web3 app. Simple as that. And they’re the things actually doing the work, sending tokens, minting NFTs, running staking, handling governance votes, and firing off automated trades or other on-chain money moves without someone babysitting the process.
So what do people usually build them with? A few tools show up over and over, and each one comes with its own vibe and tradeoffs that you feel pretty fast once you’re building something real (and not just a demo you’ll delete tomorrow).
- Solidity is the big one. It’s the go-to language for Ethereum, plus a pile of Ethereum-compatible chains like Polygon, Avalanche, and BNB Chain, and because so many teams use it, you get a huge dev community, tons of examples, and frameworks that don’t feel like they’re held together with tape.
- But Rust pops up a lot too, mostly on Solana, where people call smart contract programs. ” It’s quick, it’s strict about memory stuff, and it can be a little unforgiving so you’ll usually need more specialized chops to ship comfortably, especially when the code stops being cute and starts being complex.
- And then you’ve got the frameworks: Hardhat, Found, and Truffle. These are the “build/test/deploy” workhorses basically the stuff that keeps you sane while you iterate write tests, run local networks, and push to a chain.
- Hard tends to win when you want a flexible workflow and a setup that plays nicely with a lot of common patterns. Foundry’s the speed demon that many devs end up loving once they try it. Truffle’s been around forever, and yeah, it’s older, but plenty of projects rely on it (sometimes because that’s what the repo started with, honestly).
One more thing. This part isn’t optional. Blockchain code is to change after you deploy it, so if you ship a bug or hole, you don’t just “patch prod” and move on, you’re stuck dealing with the fallout, which is why you want security and careful testing from day one.
Wallet Integration and Connectivity
Wallet integration sits at the center of most Web3 apps. Period. Wallets aren’t just “a place to stash stuff”; they basically double as your identity and your permission slip, and every on-chain action still comes down to the user approving it by signing with cryptography (yeah, that part’s non-negotiable).
Here are the wallet pieces people usually build. And they’re not optional.
- WalletConnect: This lets an iOS hook up with wallets people already use, like MetaMask, Trust Wallet, and plenty of others. So users don’t have to switch tools or “over,” and you get fewer weird compatibility headaches across different wallet choices.
- In-app embedded wallets: These aim to cut the setup pain. Short: fewer steps. Instead of telling someone to go download an external wallet, set it up, save a seed phrase, and come back, the app spins up and handles a wallet flow inside the app itself, which is cleaner for honestly less intimidating for people who don’t consider themselves “crypto people” (which is most people).
- Multi-wallet support: People are picky. One person swears by MetaMask, another only touches Coinbase Wallet, someone else sticks with Trust Wallet, and if you force one option, you’re basically choosing to lose users. Multi-wallet support keeps the app usable for the biggest groups without turning wallet choice into a blocker.
But here’s the part teams learn the hard way: wallet UX makes or breaks a Web3 iOS app. If connecting feels sketchy, if signing screens look confusing, or if users can’t tell what they’re approving, they flee. So, what’s the point of a great app if the wallet step scares everyone off?
Decentralized Storage and Indexing
A common misunderstanding is that Web3 apps store everything on the blockchain. In reality, storing large data on-chain is expensive and slow. That’s why Web3 apps use decentralized storage systems for files, media, and metadata.
Popular solutions include:
- IPFS (InterPlanetary File System): IPFS is widely used for decentralized file storage. NFT assets such as images, videos, and metadata are often stored on IPFS instead of directly on the blockchain.
- Filecoin / Arweave: These platforms provide more persistent storage options:
- Filecoin supports decentralized storage markets and long-term storage
- Arweave focuses on permanent data storage (“pay once, store forever”)
- The Graph: The Graph is used for indexing blockchain data and making it searchable. Instead of scanning the blockchain manually for transactions, The Graph helps apps fetch structured data quickly similar to querying a database.
This stack ensures Web3 apps can remain decentralized while still being fast and scalable for real users.
Latest Trends Influencing Web3 iOS App Development
The Web3 ecosystem is evolving quickly, and iOS users now expect experiences that are fast, secure, and as easy to use as traditional apps. That’s why modern Web3 iOS App Development is no longer just about blockchain integration; it is equally about usability, accessibility, and trust.
Below are the most important trends shaping the future of Web3 iOS apps.
Multi-Chain and Cross-Chain Experiences
Back then, most Web3 apps picked one chain and stayed there. But that setup doesn’t cut it anymore, because people bounce between Ethereum, Polygon, Solana, BNB Chain, and Avalanche, moving tokens around, chasing cheaper transactions, and jumping into whatever ecosystem has the thing they want right now (and yeah, that changes week to week). So what do users actually expect? Options. Lower fees. And the freedom to move their assets wherever it makes sense.
Because of this shift, iOS Web3 apps are increasingly being built with multi-chain support, allowing users to:
- Connect and operate across multiple blockchains
- Use token bridging for moving assets between networks
- Perform cross-chain transfers without leaving the app
- View tokens and NFTs through multi-network asset dashboards
This trend is important because multi-chain capability makes Web3 apps more inclusive, scalable, and user-friendly, especially for users who diversify their holdings across different ecosystems.
NFTs Evolving Beyond Collectibles
NFTs are no longer limited to digital artwork or collectibles. Businesses are now using NFTs as a practical digital tool that provides value through ownership, access, and personalization.
In modern Web3 iOS applications, NFTs are being used for:
- Membership and subscription access (token-gated communities and premium features)
- Event ticketing with fraud-resistant verification
- Digital commerce ownership proofs, especially for luxury goods or exclusive items
- Loyalty and reward programs where NFTs unlock benefits and discounts
- Gaming asset ownership, allowing players to truly own and trade in-game items
This evolution expands the commercial potential of NFT-based products. Instead of being a trend, NFTs are becoming a long-term business model that supports engagement, retention, and monetization for Web3 iOS apps.
Web3 Security-First Development
Security remains one of the biggest challenges preventing mass adoption of Web3. Users hesitate to interact with blockchain apps due to threats like wallet hacks, phishing attacks, malicious smart contracts, and stolen private keys.
That’s why new Web3 iOS apps are adopting a security-first development approach, focusing on:
- Smart contract risk reduction through safer code practices and audits
- Secure transaction signing to prevent unauthorized approvals
- Anti-phishing mechanisms such as wallet warnings and domain verification
- Biometric protection using Face ID / Touch ID
- Strong wallet session controls, including auto-expiry and session restrictions
Apps that prioritize security are more likely to gain long-term user trust. In Web3, trust is one of the strongest competitive advantages, and better protection directly impacts retention and adoption.
Web2-Style Onboarding
One of the biggest reasons Web3 apps lose users is complicated onboarding. Traditional Web3 setups often require installing wallets, managing seed phrases, and understanding gas fees, all of which create friction for new users.
To solve this, modern Web3 iOS App Development is shifting toward onboarding that feels like Web2, including:
- Email- or phone-based login
- Social authentication (Google, Apple ID, etc.)
- Embedded wallet creation inside the app
- Seedless experience, where users don’t need to manage complex recovery phrases
This trend is critical because frictionless onboarding increases conversions and improves first-time user experience. The future of Web3 iOS apps will be defined by platforms that make blockchain features feel simple and familiar, without compromising on security.
How iTechnolabs Helps You Build Web3 iOS Apps
Building a Web3 iOS app isn’t just “make an app, ship it.” It takes real skill in two pretty different worlds, iOS engineering and blockchain work, and getting them to play nice together can get weird fast. And once you toss Web3 into the mix, teams run into headaches like wallet connections, token setup, how users actually approve and send transactions, smart contract safety, and the whole decentralized backend thing (which never feels as it sounds).
iTechnolabs provides end-to-end support for Web3 iOS App Development with a structured and scalable approach.
Strategy and product planning
Before development begins, iTechnolabs helps define:
- Business goals and product roadmap
- Feature prioritization based on use case
- Web3 monetization models
- Network selection and technical architecture
UI/UX for Web3
Web3 features often feel complex to users, so interface design matters heavily. iTechnolabs focuses on:
- Clean and intuitive UI patterns
- Simplified transaction flows
- Easy onboarding journeys
- Clear confirmation screens and wallet interactions
Smart contract development and testing
For Web3 apps, smart contracts must be secure and reliable because they directly handle transactions and asset ownership.
Development includes:
- Smart contract creation and deployment
- Testing automation
- Integration with iOS front-end
- Support for auditing workflows
Wallet and blockchain integrations
iTechnolabs integrates:
- WalletConnect support
- Embedded wallet functionality
- Token and NFT transactions
- Real-time blockchain data sync
- Secure signing and authentication
Deployment and support
After development, iTechnolabs supports:
- Performance testing
- Security validation
- App Store readiness
- Post-launch upgrades and scalability improvements
This approach ensures Web3 apps are not only launched successfully but are also scalable and secure.
The Future of Web3 iOS Apps: Decentralized Identity (DID)
Decentralized Identity (DID) is starting to feel like one of the Web3 ideas that might actually stick, especially on phones. It flips the usual setup on its head; people keep control of their own credentials and don’t have to route everything through some big, centralized identity provider (which, honestly, has been the default for way too long).
What is DID?
DID allows users to create an identity that:
- Is owned by the user
- Can be verified without revealing unnecessary data
- Works across multiple platforms and services
- Minimizes risk of identity theft
Instead of storing user identity inside centralized databases, DID systems allow identity verification through cryptographic proofs.
Why DID is important for iOS Web3 apps
DID is expected to become a standard feature in many Web3 apps due to its ability to support:
- Passwordless login
- Private KYC and identity verification
- Fraud-resistant authentication
- Cross-platform identity portability
- Better user privacy and data control
DID use cases in Web3 iOS applications
DID can power applications across industries, such as:
- Fintech apps requiring identity validation
- Healthcare apps requiring patient data privacy
- Education apps issuing certificates
- Enterprise apps for secure employee access
- DAO platforms for governance participation
As privacy concerns grow globally, DID will play a central role in the next generation of Web3 iOS App Development.
Conclusion
Web3 is turning into a whole new kind of app ecosystem, one where decentralization actually matters, transactions stay visible, and users keep control of their own. Big shift. And if you’re a business trying to build something real on blockchain, Web3 iOS app development opens doors fast: DeFi apps, NFT marketplaces, wallets, token-based communities, and even decentralized identity tools that don’t force people to hand over their life story.
But shipping a Web3 iOS app that doesn’t fall apart takes more than hype. You need a plan. A solid, up-to-date stack. Security that’s baked in from the start, not slapped on later (because yeah, attackers won’t wait). And you also need someone who knows blockchain implementation in the messy, practical sense, smart contracts, key management, audits, backend plumbing, and the whole thing, which is exactly why partnering with an experienced iOS application development company can make or break the outcome.
So what’s coming next? Account abstraction, DID, and other newer pieces are starting to make iOS Web apps feel less like a science project and more like a smooth product people will actually use. And that means better privacy, fewer “gotchas,” and experiences that put users first, without making them memorize seed phrases like it’s a weird initiation ritual.
If you’re thinking about building a Web3 iOS app that won’t look outdated in six months, iTechnolabs can handle the design, development, and launch, and they’ll keep scalability in mind while blending iOS know-how with blockchain engineering (which is where a lot of teams trip up) as a full-service iOS application development company.
FAQs
What is Web3 iOS App Development?
Web3 iOS App Development is the process of building iPhone and iPad applications that connect to blockchain networks. These apps use wallets, smart contracts, and decentralized storage to enable features like token transactions, NFTs, DeFi services, and user-owned digital identities, rather than relying only on centralized servers.
Which blockchain is best for Web3 iOS app development?
The best blockchain for Web3 iOS App Development depends on your app goals. Ethereum is ideal for mature DeFi ecosystems, Polygon offers lower fees and scalability, Solana provides fast transactions, and Avalanche or BNB Chain support high-performance apps. Most projects also adopt multi-chain support.
Do Web3 iOS apps require wallets like MetaMask?
Yes, most Web3 iOS App Development projects require wallet integration because wallets sign transactions and confirm ownership. Many apps use WalletConnect to connect MetaMask, Trust Wallet, or Coinbase Wallet. Some projects also add embedded wallets to simplify onboarding for non-crypto users.
Is Web3 iOS App Development secure for users?
Web3 iOS App Development can be secure if built properly with strong cryptography, verified smart contracts, and safe wallet handling. Apps should implement biometric login, secure session controls, anti-phishing protection, and contract audits. Security-first development is essential because blockchain transactions are irreversible.
What are the biggest challenges in Web3 iOS App Development?
The biggest challenges in Web3 iOS App Development include wallet onboarding, smart contract security, gas fee management, and cross-chain compatibility. Many users also struggle with seed phrases and transaction confirmations. That’s why modern apps focus on Web2-style onboarding and improved UX.